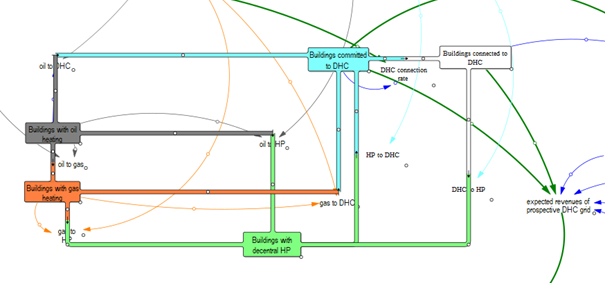
In a previous News Article, a qualitative model of thermal grid implementation dynamics in cities and municipalities was described. As a step forward, a quantitative, dynamic model, named SCOVILLE (Strategy Cockpits for Orchestrated Implementation of Thermal Grids in Cities and Municipalities) has now been developed by ZHAW.
The model simulates how KPIs (i.e., annual cash flow, market share of thermal grids and speed of heating system decarbonization) respond to decision-making by building owners, public policy interventions and the utility’s pricing and financing strategies.
The SCOVILLE modeling framework is a versatile tool that can be easily parameterized to local settings and adapted to new research questions.
In the next years, for example, it will be used to simulate the effect of various innovations and policy packages on the success of municipal energy strategies.
The purpose of SCOVILLE is to:
- Enable collective reflection on the challenges and strengths of long-term strategies to develop and operate thermal grids
- Encourage participants to make their assumptions explicit through transparent model structure
- Support iterative strategic planning with a dynamic perspective
We look forward to discussing the model with research and industry partners, and to applying it to many interesting challenges of heating and cooling decarbonization.
Paper describing the conceptual background
Speich, Matthias & Ulli-Beer, Silvia (2024): Business implications of net-zero targets for district heating and cooling, Proceedings of the 2024 International System Dynamics Conference, August 4-8, 2024, Bergen, Norway
https://proceedings.systemdynamics.org/2024/papers/O1263.pdf